Wireless Questions 3
Question 1
Explanation
Output power is measured in mW (milliwatts). A milliwatt is equal to one thousandth (10−3) of a watt.
Question 2
Question 3
Explanation
+ From the output of WLC “show interface summary”, we learned that the WLC has four VLANs: 999, 14, 15 and 16.
+ From the “show ap config general FlexAP1” output, we learned that FlexConnect AP has four VLANs: 10, 11, 12 and 13. Also the WLAN of FlexConnect AP is mapped to VLAN 10 (from the line “WLAN 1: …… 10 (AP-Specific)).
From the reference at: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/8-1/Enterprise-Mobility-8-1-Design-Guide/Enterprise_Mobility_8-1_Deployment_Guide/ch7_HREA.html
FlexConnect VLAN Central Switching Summary
Traffic flow on WLANs configured for Local Switching when FlexConnect APs are in connected mode are as follows:
+ If the VLAN is returned as one of the AAA attributes and that VLAN is not present in the FlexConnect AP database, traffic will switch centrally and the client is assigned this VLAN/Interface returned from the AAA server provided that the VLAN exists on the WLC. (-> as VLAN 15 exists on the WLC so the client in connected mode would be assigned this VLAN -> Answer G is correct)
+ If the VLAN is returned as one of the AAA attributes and that VLAN is not present in the FlexConnect AP database, traffic will switch centrally. If that VLAN is also not present on the WLC, the client will be assigned a VLAN/Interface mapped to a WLAN on the WLC.
+ If the VLAN is returned as one of the AAA attributes and that VLAN is present in the FlexConnect AP database, traffic will switch locally.
+ If the VLAN is not returned from the AAA server, the client is assigned a WLAN mapped VLAN on that FlexConnect AP and traffic is switched locally.
Traffic flow on WLANs configured for Local Switching when FlexConnect APs are in standalone mode are as follows:
+ If the VLAN returned by the AAA server is not present in the FlexConnect AP database, the client will be put on a default VLAN (that is, a WLAN mapped VLAN on a FlexConnect AP) (-> Therefore answer B is correct). When the AP connects back, this client is de-authenticated (-> Therefore answer C is correct) and will switch traffic centrally.
Question 4
Question 5
Explanation
Once you know the complete combination of transmitter power level, the length of cable, and the antenna gain, you can figure out the actual power level that will be radiated from the antenna. This is known as the effective isotropic radiated power (EIRP), measured in dBm.
EIRP is a very important parameter because it is regulated by governmental agencies in most countries. In those cases, a system cannot radiate signals higher than a maximum allowable EIRP. To find the EIRP of a system, simply add the transmitter power level to the antenna gain and subtract the cable loss.
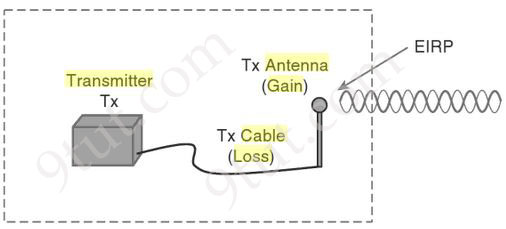
EIRP = Tx Power – Tx Cable + Tx Antenna
Suppose a transmitter is configured for a power level of 10 dBm (10 mW). A cable with 5-dB loss connects the transmitter to an antenna with an 8-dBi gain. The resulting EIRP of the system is 10 dBm – 5 dB + 8 dBi, or 13 dBm.
You might notice that the EIRP is made up of decibel-milliwatt (dBm), dB relative to an isotropic antenna (dBi), and decibel (dB) values. Even though the units appear to be different, you can safely combine them because they are all in the dB “domain”.
Reference: CCNA Wireless 640-722 Official Cert Guide
Question 6
Explanation
This is called Inter Controller-L2 Roaming. Inter-Controller (normally layer 2) roaming occurs when a client roam between two APs registered to two different controllers, where each controller has an interface in the client subnet. In this instance, controllers exchange mobility control messages (over UDP port 16666) and the client database entry is moved from the original controller to the new controller.
Question 7
Explanation
Windows can actually block your WiFi signal. How? Because the signals will be reflected by the glass.
Some new windows have transparent films that can block certain wave types, and this can make it harder for your WiFi signal to pass through.
Tinted glass is another problem for the same reasons. They sometimes contain metallic films that can completely block out your signal.
Mirrors, like windows, can reflect your signal. They’re also a source of electromagnetic interference because of their metal backings.
Reference: https://dis-dot-dat.net/what-materials-can-block-a-wifi-signal/
An incandescent light bulb, incandescent lamp or incandescent light globe is an electric light with a wire filament heated until it glows. WiFi operates in the gigahertz microwave band. The FCC has strict regulations on RFI (radio frequency interference) from all sorts of things, including light bulbs -> Incandesent lights do not interfere Wi-Fi networks.
Note:
+ Many baby monitors operate at 900MHz and won’t interfere with Wi-Fi, which uses the 2.4GHz band.
+ DECT cordless phone 6.0 is designed to eliminate wifi interference by operating on a different frequency. There is essentially no such thing as DECT wifi interference.
Question 8
Explanation
When the primary controller (WLC-1) goes down, the APs automatically get registered with the secondary controller (WLC-2). The APs register back to the primary controller when the primary controller comes back on line.
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
Directional antennas
Directional antennas come in many different styles and shapes. An antenna does not offer any added power to the signal; it simply redirects the energy it receives from the transmitter. By redirecting this energy, it has the effect of providing more energy in one direction and less energy in all other directions. As the gain of a directional antenna increases, the angle of radiation usually decreases, providing a greater coverage distance but with a reduced coverage angle. Directional antennas include patch antennas and parabolic dishes. Parabolic dishes have a very narrow RF energy path, and the installer must be accurate in aiming these types of antennas at each other.
 Directional patch antenna
Directional patch antenna
Omnidirectional antennas
An omnidirectional antenna is designed to provide a 360-degree radiation pattern. This type of antenna is used when coverage in all directions from the antenna is required. The standard 2.14-dBi “rubber duck” is one style of omnidirectional antenna.
 Omnidirectional antenna
Omnidirectional antenna
-> Therefore Omnidirectional antenna is best suited for a high-density wireless network in a lecture hall.
Question 11
Explanation
We will have the answer from this paragraph:
“TLV values for the Option 43 suboption: Type + Length + Value. Type is always the suboption code 0xf1. Length is the number of controller management IP addresses times 4 in hex. Value is the IP address of the controller listed sequentially in hex. For example, suppose there are two controllers with management interface IP addresses, 192.168.10.5 and 192.168.10.20. The type is 0xf1. The length is 2 * 4 = 8 = 0x08. The IP addresses translates to c0a80a05 (192.168.10.5) and c0a80a14 (192.168.10.20). When the string is assembled, it yields f108c0a80a05c0a80a14. The Cisco IOS command that is added to the DHCP scope is option 43 hex f108c0a80a05c0a80a14.”
Therefore in this question the option 43 in hex should be “F104.AC10.3205 (the management IP address of 172.16.50.5 in hex is AC.10.32.05).
Question 12
Explanation
At first, we thought “greater severity” means higher priority (or severity with smaller value) in the Syslog level table below:
| Level | Keyword | Description |
| 0 | emergencies | System is unusable |
| 1 | alerts | Immediate action is needed |
| 2 | critical | Critical conditions exist |
| 3 | errors | Error conditions exist |
| 4 | warnings | Warning conditions exist |
| 5 | notification | Normal, but significant, conditions exist |
| 6 | informational | Informational messages |
| 7 | debugging | Debugging messages |
For example, levels 0 to 4 are “greater severity” than level 5. But according to this Cisco link:
“If you set a syslog level, only those messages whose severity is equal to or less than that level are sent to the syslog servers. For example, if you set the syslog level to Notifications (severity level 5), only those messages whose severity is between 0 and 5 are sent to the syslog servers.”
The correct answer for this question should be “equal or less severity”.



For Question 3:
Can someone explain, below question:
G. When the AP is in connected mode, the client will be placed in VLAN 15.
■If the VLAN is returned as one of the AAA attributes and that VLAN is not present in the Flex AP database, traffic will switch centrally. If that VLAN is also not present on the WLC, the client will be assigned a VLAN/Interface mapped to a WLAN on the WLC.
Where are we getting VLAN15, as I do not see it mapped under “Config General FlexAP1”
Q2 I think the correct A, E, F
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless-mobility/wireless-lan-wlan/212576-configure-802-11w-management-frame-prote.html#anc11
On Q2 ask IOS XE!!! Not AIR OS
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/switches/lan/catalyst3650/software/release/16-1/configuration_guide/b_161_consolidated_3650_cg/b_161_consolidated_3650_cg_chapter_010010011.pdf
security pmf {association-checkassociation-comeback-time-in-seconds| mandatory | optional |saquery | saquery-time-in-milliseconds}
Q10.
Do you really think that an omnidirectional antenna is better for high-density wireless network? Please read link
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/wireless/controller/technotes/8-7/b_wireless_high_client_density_design_guide.html
THE PATHETIC most section in the exam…. what sort of questions are cisco asking.. like to convert dec into hex on paper ?…. its all memory questions .. they should ask logical ones not these types of silly memory questions….
Question 7 about the Interference, I believe the right answers are DECT Phone and Baby Monitor.
Other physical (non-metallic) objects that do NOT emit signal they do not interfere but refract the signal
There should not necessarily be a superposition of the exact frequency to have interference
https://courses.lumenlearning.com/physics/chapter/16-10-superposition-and-interference/
Please do a better research or check this question with an expert
I have done a bit more research for this and got even more confused. The question is not formed correctly, it should be more like what interferes (messes us) with the signal, because interference as a physical concept is not the same as diffraction/refraction (mirror example) or attenuation of the signal (the fish tank example)… If I get this question in the exam I will raise a complaint to them as technically none should be the correct answer…
Tunnel-Type = 13 // Virtual LANs (VLAN)
Tunnel-Medium-Type = 6 // 802
Tunnel-Private-Group-Id = 142 // Vlan ID
the last comment was the generic info explaining what does each attribute mean
Where can I see waht are the questions ? Ijust see the Explanations o fthe questions, but where are the questions?
Question 12 Answer should be letter A.
https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/wireless/4100-series-wireless-lan-controllers/107252-WLC-Syslog-Server.html
If you set a syslog level, only those messages whose severity is equal to or less than that level are sent to the syslog servers. For example, if you set the syslog level to Notifications (severity level 5), only those messages whose severity is between 0 and 5 are sent to the syslog servers.
@asdf: Yes, thanks for your detection, we updated Q12!
@digitaltut On Question 12
Refer to the exhibit. Which level message does the WLC send to the syslog server?
A is correct here, but on the short composite quiz, I got marked wrong when I chose A:
A. syslog level errors and less severity messageswrong
B. syslog level errors and greater severity messagescorrect
C. all syslog levels messages
D. syslog level errors messages
What’s the right answer then? Can you sync them with the correct answer, TIA.
@blue: The correct answer should be “syslog level errors and less severity message”. We corrected the quiz answer. Could you please try again?
@digitaltut
I found this question in another study guide. Can you guys verify the question and it’s supposed answer:
404.A customer has a pair of Cisco 5520 WLCs set up in an SSO cluster to manage all APs. Guest traffic
is anchored to a Cisco 3504 WLC located in a DMZ.
Which action is needed lo ensure that the EoIP tunnel remains in an (JP slate in the event of failover on
the SSO duster?
A. Enable default gateway reachability check.
B. Configure back-lo-badt connectivity on the RP ports.
C. Use the same mobility domain on all WLCs.
D. Use the mobility MAC when the mobility peer is configured
Answer: C
12 is D for sure.
I am not sure the wording of the question is correct. I think it should be attenuation not interference
Question 7
Which two sources cause interference for Wi-Fi networks? (Choose two)
A. mirrored wall
B. fish tank
C. 900MHz baby monitor
D. DECT 6.0 cordless
E. incandesent lights
Answer: A B
@digitaltut, Q6 does have wrong wording. There should be VLAN (in both, picture and question) not WLAN. Question nor the picture does not make any sense with Wireless LAN (WLAN) as controllers cannot be “in the same WLAN” but they can be “in the same VLAN”. With VLAN it does make perfect sense.
VLAN = Virtual LAN – L2 separated LAN segment / L2 broadcast domain (Usually 802.1q separated on trunk)
WLAN =Wireless LAN = Usually refer to sum of SSID settings in Cisco terminology pushed from WLC to LAPs
Clients are connecting to SSID broadcasted by LAP on WLC we will than see that cliet’s are connected to particular WLAN.
Picture WLC===WLAN===WLC does not make senese. Controllers cannot be connected via WLAN. However WLC===VLAN===WLC does make much more sense as both WLCs could be connected to the same VLAN = sharing the same L2 segment / broadcast domain = when Client roams from one WLC to another he can be switched to the L2 segment by new WLC without any issues and WLCs just update their client table. (There are few requirements for this to work flawlessly like WLC must be in the same mobility group etc… but this question is not that specific – maybe on real exam it has more verbiage)
Thank you
@NX: Thank you for your detection, we updated Q6!
I agree with @KenWood.
Question 12 The answer should be D. syslog level errors and greater severity messages. Please kindly review this question.
If you set a syslog level, only those messages whose severity is equal to or less than that level are sent to the syslog servers. For example, if you set the syslog level to Notifications (severity level 5), only those messages whose severity is between 0 and 5 are sent to the syslog servers.
(0 is emergency, 1 is alerts, 2. critical 3.errors 4 warnings 5.notification) . Level 0-4 are greater severity than level 5. Q 12 set the syslog servers to error (level 3), so level 0 – 3 will be sent to syslog server. 0, 1, 2 are greater severity than 3 (Error).
Level Keyword Description
0 emergencies System is unusable
1 alerts Immediate action is needed
cficant, conditions exist
6 informational Informational messages
7 debugging Debugging messages
You are configuring a controller that runs Cisco IOS XE by using the CLI. Which three configuration options are used for 802.11w Protected Management Frames? (Choose three)
A. mandatory
B. association-comeback
C. SA teardown protection
D. saquery-retry-time
E. enable
F. comeback-time
Answer ACE