SD-WAN & SD-Access Solutions
|
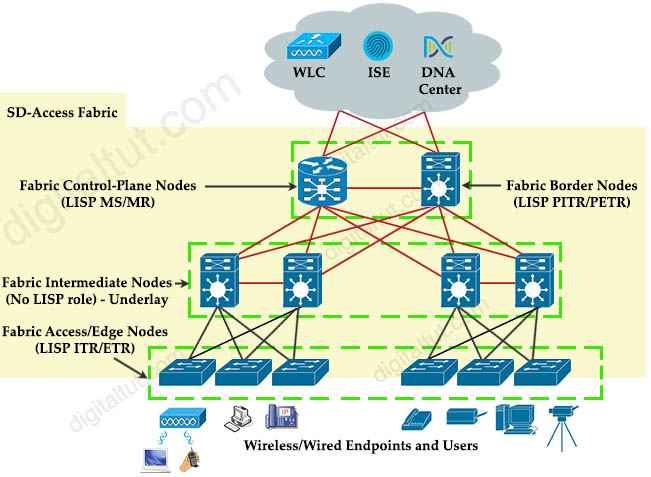
SD-Access Quick summary There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:
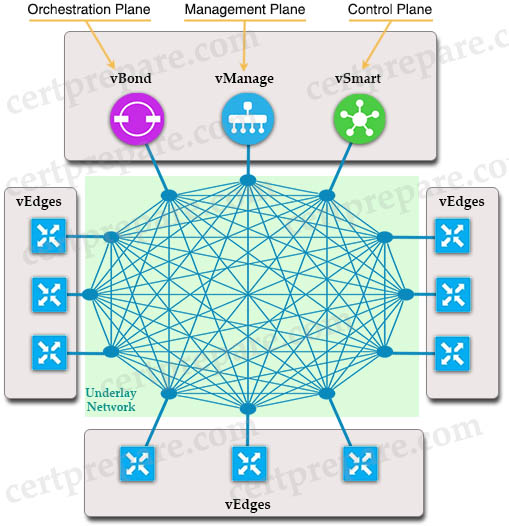
The border node and control plane nodes are the equivalents of the core; the intermediate nodes are the equivalent of the distribution layer; and the edge nodes are the equivalent to the access layer. Three major building blocks that make up SDA: the control plane, the data plane and the policy plane. + Control-Plane based on LISP SD-WAN Quick Summary The primary components for the Cisco SD-WAN solution consist of the vManage network management system (management plane), the vSmart controller (control plane), the vBond orchestrator (orchestration plane), and the vEdge router (data plane). + vManage – This centralized network management system provides a GUI interface to easily monitor, configure, and maintain all Cisco SD-WAN devices and links in the underlay and overlay network. + vSmart controller – This software-based component is responsible for the centralized control plane of the SD-WAN network. It establishes a secure connection to each vEdge router and distributes routes and policy information via the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP), acting as a route reflector. It also orchestrates the secure data plane connectivity between the vEdge routers by distributing crypto key information, allowing for a very scalable, IKE-less architecture. + vBond orchestrator – This software-based component performs the initial authentication of vEdge devices and orchestrates vSmart and vEdge connectivity. It also has an important role in enabling the communication of devices that sit behind Network Address Translation (NAT). + vEdge router – This device, available as either a hardware appliance or software-based router, sits at a physical site or in the cloud and provides secure data plane connectivity among the sites over one or more WAN transports. It is responsible for traffic forwarding, security, encryption, Quality of Service (QoS), routing protocols such as Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and more.
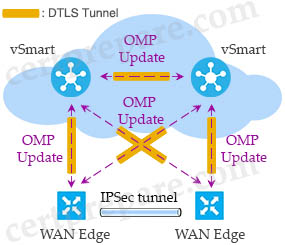
Cisco SD-WAN uses Overlay Management Protocol (OMP) which manages the overlay network. OMP runs between the vSmart controllers and WAN Edge routers (and among vSmarts themselves) where control plane information, such as the routing, policy, and management information, is exchanged over a secure connection.
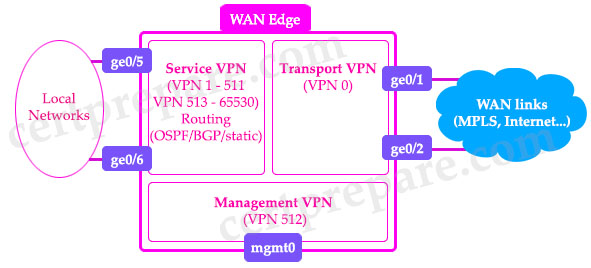
VPNs in SD-WAN In the SD-WAN overlay, virtual private networks (VPNs) provide segmentation. Each VPN is equivalent to a VRF, which is isolated from one another and have their own forwarding tables. An interface or subinterface is explicitly configured under a single VPN and cannot be part of more than one VPN. Devices attached to an interface in one VPN cannot communicate with devices in another VPN unless policy is put in place to allow it. The VPN ranges from 0 to 65535, but several VPNs are reserved for internal use. The Transport & Management VPNs There are two implicitly configured VPNs in the WAN Edge devices and controllers: VPN 0 and VPN 512. – VPN 0 is the transport VPN. It contains all the interfaces that connect to the WAN links. Secure DTLS/TLS connections to the controllers are initiated from this VPN. Static or default routes or a dynamic routing protocol needs to be configured inside this VPN in order to get appropriate next-hop information so the control plane can be established and IPsec tunnel traffic can reach remote sites. VPN 0 connects the WAN Edge to the WAN transport and creates control plane and data plane connections. The WAN Edge device can connect to multiple WAN transport(s) on different interfaces on the same VPN 0 transport segment. At least one interface needs to be configured to initially reach the SD-WAN controllers for onboarding. – VPN 512 is the management VPN. It carries the out-of-band management traffic to and from the Cisco SD-WAN devices. This VPN is ignored by OMP and not carried across the overlay network.
|
Question 1
Explanation
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:
+ Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for
the fabric overlay.
+ Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
Question 2
Explanation
+ Orchestration plane (vBond) assists in securely onboarding the SD-WAN WAN Edge routers into the SD-WAN overlay (-> Therefore answer A mentioned about vBond). The vBond controller, or orchestrator, authenticates and authorizes the SD-WAN components onto the network. The vBond orchestrator takes an added responsibility to distribute the list of vSmart and vManage controller information to the WAN Edge routers. vBond is the only device in SD-WAN that requires a public IP address as it is the first point of contact and authentication for all SD-WAN components to join the SD-WAN fabric. All other components need to know the vBond IP or DNS information.
+ Management plane (vManage) is responsible for central configuration and monitoring. The vManage controller is the centralized network management system that provides a single pane of glass GUI interface to easily deploy, configure, monitor and troubleshoot all Cisco SD-WAN components in the network. (-> Answer C and answer D are about vManage)
+ Control plane (vSmart) builds and maintains the network topology and make decisions on the traffic flows. The vSmart controller disseminates control plane information between WAN Edge devices, implements control plane policies and distributes data plane policies to network devices for enforcement (-> Answer B is about vSmart)
Question 3
Explanation
The southbound protocol used by APIC is OpFlex that is pushed by Cisco as the protocol for policy enablement across physical and virtual switches.
Southbound interfaces are implemented with some called Service Abstraction Layer (SAL), which talks to the network elements via SNMP and CLI.
Note: Cisco OpFlex is a southbound protocol in a software-defined network (SDN).
Question 4
Explanation
Today the Dynamic Network Architecture Software Defined Access (DNA-SDA) solution requires a fusion router to perform VRF route leaking between user VRFs and Shared-Services, which may be in the Global routing table (GRT) or another VRF. Shared Services may consist of DHCP, Domain Name System (DNS), Network Time Protocol (NTP), Wireless LAN Controller (WLC), Identity Services Engine (ISE), DNAC components which must be made available to other virtual networks (VN’s) in the Campus.
Question 5
Explanation
Fabric mode APs continue to support the same wireless media services that traditional APs support; apply AVC, quality of service (QoS), and other wireless policies; and establish the CAPWAP control plane to the fabric WLC. Fabric APs join as local-mode APs and must be directly connected to the fabric edge node switch to enable fabric registration events, including RLOC assignment via the fabric WLC. The fabric edge nodes use CDP to recognize APs as special wired hosts, applying special port configurations and assigning the APs to a unique overlay network within a common EID space across a fabric. The assignment allows management simplification by using a single subnet to cover the AP infrastructure at a fabric site.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/Campus/sda-sdg-2019oct.html
Question 6
Explanation
The tunneling technology used for the fabric data plane is based on Virtual Extensible LAN (VXLAN). VXLAN encapsulation is UDP based, meaning that it can be forwarded by any IP-based network (legacy or third party) and creates the overlay network for the SD-Access fabric. Although LISP is the control plane for the SD-Access fabric, it does not use LISP data encapsulation for the data plane; instead, it uses VXLAN encapsulation because it is capable of encapsulating the original Ethernet header to perform MAC-in-IP encapsulation, while LISP does not. Using VXLAN allows the SD-Access fabric to support Layer 2 and Layer 3 virtual topologies (overlays) and the ability to operate over any IP-based network with built-in network segmentation (VRF instance/VN) and built-in group-based policy.
Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide
Question 7
Explanation
Access Points
+ AP is directly connected to FE (or to an extended node switch)
+ AP is part of Fabric overlay
Reference: https://www.ciscolive.com/c/dam/r/ciscolive/us/docs/2018/pdf/BRKEWN-2020.pdf
Question 8
Explanation
The primary components for the Cisco SD-WAN solution consist of the vManage network management system (management plane), the vSmart controller (control plane), the vBond orchestrator (orchestration plane), and the vEdge router (data plane).
+ vManage – This centralized network management system provides a GUI interface to easily monitor, configure, and maintain all Cisco SD-WAN devices and links in the underlay and overlay network.
+ vSmart controller – This software-based component is responsible for the centralized control plane of the SD-WAN network. It establishes a secure connection to each vEdge router and distributes routes and policy information via the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP), acting as a route reflector. It also orchestrates the secure data plane connectivity between the vEdge routers by distributing crypto key information, allowing for a very scalable, IKE-less architecture.
+ vBond orchestrator – This software-based component performs the initial authentication of vEdge devices and orchestrates vSmart and vEdge connectivity. It also has an important role in enabling the communication of devices that sit behind Network Address Translation (NAT).
+ vEdge router – This device, available as either a hardware appliance or software-based router, sits at a physical site or in the cloud and provides secure data plane connectivity among the sites over one or more WAN transports. It is responsible for traffic forwarding, security, encryption, Quality of Service (QoS), routing protocols such as Border Gateway Protocol (BGP) and Open Shortest Path First (OSPF), and more.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/dam/en/us/td/docs/solutions/CVD/SDWAN/CVD-SD-WAN-Design-2018OCT.pdf
Question 9
Question 10
Explanation
There are five basic device roles in the fabric overlay:
+ Control plane node: This node contains the settings, protocols, and mapping tables to provide the endpoint-to-location (EID-to-RLOC) mapping system for the fabric overlay.
+ Fabric border node: This fabric device (for example, core layer device) connects external Layer 3 networks to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric edge node: This fabric device (for example, access or distribution layer device) connects wired endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Fabric WLAN controller (WLC): This fabric device connects APs and wireless endpoints to the SDA fabric.
+ Intermediate nodes: These are intermediate routers or extended switches that do not provide any sort of SD-Access fabric role other than underlay services.

Reference: CCNP and CCIE Enterprise Core ENCOR 350-401 Official Cert Guide



Question 7
Which description of an SD-Access wireless network infrastructure deployment is true?
A. The access point is part of the fabric underlay
B. The WLC is part of the fabric underlay
C. The access point is part the fabric overlay
D. The wireless client is part of the fabric overlay
Should be C. The access point is part the fabric overlay? correct?
I don’t think so, an AP can’t be part of the overlay.
Take a look at the OCG. You have to study all the topic before ….
Sorry Ciscolad,
I think you are right : Access Points
AP is directly connected to FE (or to an extended node switch)
AP is part of Fabric overlay
AP belongs to the INFRA_VN which is mapped to the global routing
table (new in DNAC 1.1)
AP joins the WLC in Local mode
here the link where i find it
https://connectandsecure2019.nl/wp-content/uploads/2019/05/Connect-Secure-2019-SD-Access-Jesse-Schmidt.pdf
Which action is the vSmart controller responsible for in an SD-WAN deployment?
A. onboard vEdge nodes into the SD-WAN fabric
B. distribute security information for tunnel establishment between vEdge routers
C. manage, maintain, and gather configuration and status for nodes within the SD-WAN fabric
D. gather telemetry data from vEdge routers
Is there A anser right? It’s looks some strange… What does it mean?
Which action is the vSmart controller responsible for in an SD-WAN deployment?
A. onboard vEdge nodes into the SD-WAN fabric
B. distribute security information for tunnel establishment between vEdge routers
C. manage, maintain, and gather configuration and status for nodes within the SD-WAN fabric
D. gather telemetry data from vEdge routers
B is right
Which action is the vSmart controller responsible for in an SD-WAN deployment?
A. onboard vEdge nodes into the SD-WAN fabric
B. distribute security information for tunnel establishment between vEdge routers
C. manage, maintain, and gather configuration and status for nodes within the SD-WAN fabric
D. gather telemetry data from vEdge routers
B is right
*******
vSmart controller – This software-based component is responsible for the centralized control plane of the SD-WAN network. It establishes a secure connection to each vEdge router and distributes routes and policy information via the Overlay Management Protocol (OMP), acting as a route reflector.
A. vBond
B. vSmart
C+D. vManage
Does anyone has SD-WAN (300-415) dumps.
Which statement about a Cisco APIC controller versus a more traditional SDN controller is true?
A. APIC uses a policy agent to translate policies into instructions
B. APIC supports OpFlex as a Northbound protocol
C. APIC does support a Southbound REST API
D. APIC uses an imperative model
I think its “A” but not completely sure. I don’t think its “B” because Cisco OpFlex is a southbound protocol in a software-defined network (SDN). Is this correct?
Dear all fri/brothers,
Did anyone has exam ENCOR (300-415) in this afew days. Do they have new question ?
Pls kindly feel free share me because I will exam in next afew days. Big thank you in advance
I don’t think question #2 is the B. For me the best answer for this question is the A.
This is the reason:
The major components of the vBond orchestrator are:
Control plane connection—Each vBond orchestrator has a persistent control plane connection in the form of a DTLS tunnel with each vSmart controller in its domain. In addition, the vBond orchestrator uses DTLS connections to communicate with vEdge routers when they come online, to authenticate the router, and to facilitate the router’s ability to join the network. Basic authentication of a vEdge router is done using certificates and RSA cryptography.
Authentication—The vSmart controller has pre-installed credentials that allow it to authenticate every new vEdge router that comes online. These credentials ensure that only authenticated devices are allowed access to the network.
Source: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs-book/system-overview.html
Q2
The vBond orchestrator orchestrates the initial control connection between vSmart controllers and vEdge routers. It creates DTLS tunnels to the vSmart controllers and vEdge routers to authenticate each node that is requesting control plane connectivity. This authentication behavior assures that only valid customer nodes can participate in the Cisco SD-WAN overlay network. The DTLS connections with vSmart controllers are permanent so that the vBond controller can inform the vSmart controllers as vEdge routers join the network. The DTLS connections with vEdge routers are temporary; once the vBond orchestrator has matched a vEdge router with a vSmart controller, there is no need for the vBond orchestrator and the vEdge router to communicate with each other.
That means that the tunnel between vBond and vEdges is just for authentication (Onboard vEdge nodes), after that the tunnel is ended. So I think answer A is for vBond.
Source: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/td/docs/routers/sdwan/configuration/sdwan-xe-gs-book/system-overview.html
Thanks for the article
https://www.thenetworkdna.com/search/label/Viptela%20SDWAN?&max-results=7
Hi guys,
The ENCOR exam have not any labs?
Can anyone help me with the questions? Thank You.
where i can find questions?
i am so satisfacted.my english is poor, sorry :). thx for approving my user greetings wally
Anyone please guide..is there any simulation based lab in ENCORE exam…someone told me there is no simulation in ENCORE 300-401???
Why aren’t the questions showing?
Ich bin gegen covid 19. Was ist deine Meinung? mituns
HI Guys. Thanks for my approving / wazz user, new user hehe
Q10.
Where do ISE and DNA-C belong to, if not in the fabric overlay?
@Wumpe
Don’t know but does not matter as I guess the question is about the roles not where they belong to!
How do I move a thread to a different topic?
hi all :)
So what are the correct answers for these questions?
When a wired client connects to an edge switch in an SDA fabric, which component decides whether the client has access to the network?
Which statement about a Cisco APIC controller versus a more traditional SDN controller is true?
Not sure about the right answers yet.
I can’t see the questions, only the solutions. Is there any way of fiixing this?
After long time, I am back to digitaltut, This was helped me to clear my Cisco All certification, Past 6 years i didnt came to this site and My certificate expired 2 years before, I am back still site was active surprise, Very good site with clear explanation, I am planning for CCNP ENCOR and CCIE Enterprise, Do we have any recently took this certification with help of this site.
I have start my journey again from here.
Can anyone share me dump and questions above ? I will take the exam next week
mincukho at gmail dot com
do you have answers to the digital learning for CE credits?
Why are there no questions?
Part 5 Q41 and this part Q8 is the same questions but the answers are different.
It should be vBond.
There are pictures missing from SD-Access Quick summary
There are pictures missing from SD-Access Quick summary
I don’t see any questions in this site.. only explanation
Q4. Answer: A
Fusion Router focuses on the connection between the SD-Access fabric and the traditional IP network, handling traffic translation and providing access to external resources. On the other hand, the Border Node is primarily responsible for route leaking and connectivity within the SD-Access fabric, enabling communication between user-defined VNs and shared services while enforcing policies and isolation.
Question 7
Which description of an SD-Access wireless network infrastructure deployment is true?
A. The access point is part of the fabric underlay
B. The WLC is part of the fabric underlay
C. The access point is part the fabric overlay
D. The wireless client is part of the fabric overlay
Answer: C – Wrong. The true answer is A. C and D are the same, therefore, C cannot be the answer. In addition, AP is part of the fabric underlay because they provide the wireless connectivity that allows endpoints to access the SD-Access fabric.
Question 7 is underlay. Wireless and AP’s are part of the underlay.
Cisco SD-WAN has been rebranded in 2023 and from Cisco IOS-XE SD-WAN release 127.12.1.a and Cisco Catalyst SD-WAN release 20.12.1 you’ll see different names. Unsure if the exam has the updated names yet.
vManage is now called Manager
vAnalytics is now called Analytics
!vBond is now called Validator!
!vSmart is now called Controller!
Hello guys, anyone who did the exam in late 2024 or 2025, are the dumps still valid, I am sitting fro the exams in a few days, please advise :-)
ANYONE PASSED THE EXAMN WITH QUESTIONS FROM HERE?