OSPF Questions 9
Here you will find answers to OSPF Questions – Part 9
Question 1
In IPv6, the interfaces running OSPF can be configured with multiple address prefixes. Which statement is true about the IPv6 addresses that can be included into the OSPF process?
A. Specific addresses cannot be selected for importation into the OSPF process.
B. Specific addresses can be selected using an ACL.
C. Specific addresses can be selected using a route map.
D. Specific addresses can be selected using a prefix list.
Answer: A
Explanation
When importing (redistributed) a set of addresses specified on an interface on which OSPFv3 is running into OSPFv3, you cannot select specific addresses to be imported. Either all addresses are imported, or no addresses are imported.
Question 2
Which statement is true about the command ipv6 ospf 1 area 0?
A. It must be issued in router global configuration mode to enable the OSPF process for IPv6.
B. It must be issued in interface configuration mode to enable the OSPF process for IPv6.
C. It must be issued before the network command to enable the OSPF process for IPv6.
D. It must be issued after the network command to enable the OSPF process for IPv6.
Answer: B
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Based on the output from the show command on RT1 which statement is true?

A. OSPFv3 uses global IPv6 addresses to establish neighbor adjacencies.
B. RT1 has a subnet mask of 64 bits.
C. RT1 has FastEthernet0/0 set as a DR for network type broadcast.
D. OSPFv3 uses Link-local addresses to establish neighbor adjacencies.
E. RT1 does not have a global IPv6 address set on FastEthernet0/0.
F. OSPFv3 uses IPv4 addresses to establish neighbor adjacencies.
Answer: D
Explanation
Link local address is a special type of address intended for communications within the local network segment or a point-to-point connection. Routers do not forward packets with link local address. The link local address gets a FE80::/10 prefix.
The OSPFv3 uses Link-local address to form neighbor adjacency by sending and receiving the hello packet to the neighbor router.
Question 4
What command should be used for a totally stubby area on the router connected to area 0 backbone?
A. totally stubby on the ABR
B. stub no-summary on the ABR
C. totally stubby on all routers in the area
D. stub no-summary on the ASBR
E. stub no-summary on all routers in the area
F. totally stubby on the ASBR
Answer: B
Question 5
Refer to the output. What IOS command produces this output?
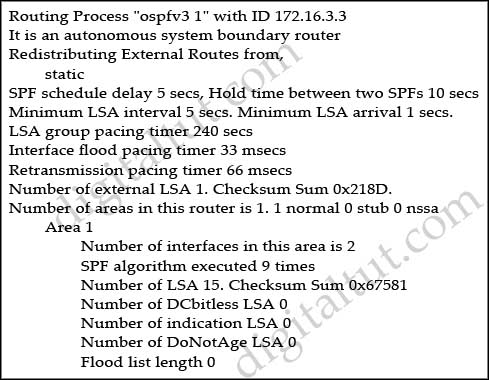
A. show ip ospf
B. show ip ospf interface
C. show ipv6 ospf interface
D. show ipv6 ospf
Answer: D
Explanation
The command “show ipv6 ospf” is used to display general information about OSPF routing processes.
Question 6
Which three statements are true when configuring redistribution for OSPF? (Choose three)
A. The default metric is 10.
B. The default metric is 20.
C. The default metric type is 2.
D. The default metric type is 1.
E. Subnets do not redistribute by default.
F. Subnets redistribute by default.
Answer: B C E
Question 7
To create an NSSA totally stubby area in Area 1, what commands should be configured on the NSSA ABR?
A. router ospf 1
area 1 nssa
B. router ospf 1
area 1 nssa no-summary
C. router ospf 1
area 1 nssa no-redistribution
D. router ospf 1
area 1 nssa default-information originate
E. router ospf 1
area 1 nssa default-information originate metric-type 2
Answer: B
Question 8
How is the configuration of a totally stubby area different from that of a stub area?
A. The totally stubby area requires the no-summary command on the ABR.
B. The totally stubby area requires the totally stubby command on the ABR.
C. The no-summary command should be included on all routers within the totally stubby area.
D. The totally stubby command should be included on all routers within the totally stubby area.
E. The totally stubby area requires the no-summary command on the ASBR.
Answer: A
Question 9
Which three statements about configuring OSPF in a IPv6 network are true? (Choose three)
A. OSPF version 2 will support IPv6.
B. OSPF version 3 will support IPv6.
C. Multiple instances of OSPF for IPv6 can be run on a link.
D. Networks must be explicitly configured using the network command in router OSPF configuration mode.
E. IPv4 addresses cannot be used as the router ID in OSPF for IPv6.
F. The interface command ipv6 ospf area is all that is required to enable OSPF for IPv6 on an interface.
Answer: B C F
Question 10
In which state do DR and BDR establish adjacency with each OSPF router in the network?
A. Init State
B. Exstart State
C. Exchange State
D. Loading State
Answer: A
Explanation
When OSPF adjacency is formed, a router goes through several state changes before it becomes fully adjacent with its neighbor. The states are: Down, Attempt, Init, 2-Way, Exstart, Exchange, Loading, and Full.
Suppose two routers are just turned on and want to establish DR\BDR adjacency. Both are in DOWN state, each router sends a multicast Hello and moves to INIT state. After a router has both received a Hello and verified that all the required parameters agree, the router lists the other router’s RID in the Hello message as being seen. When a router receives a Hello that lists its own RID as having been seen by the other router, the router can transition to 2-Way state.
(Reference: CCNP ROUTE 642-902 Official Certification Guide)



according to Q3, can’t answer E be correct? from this show output we actually don’t know global ipv6 address set or not?