NTP Questions
|
Quick review of NTP NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source, usually a reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard.
A stratum 2 server is connected to the stratum 1 server; then a stratum 3 server is connected to the stratum 2 server and so on. A stratum 2 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum 1 server. A stratum 3 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum-2 server… A stratum server may also peer with other stratum servers at the same level to provide more stable and robust time for all devices in the peer group (for example a stratum 2 server can peer with other stratum 2 servers). – NTP is designed to synchronize the time on a network. NTP runs over the User Datagram Protocol (UDP), using port 123 as both the source and destination. |
Question 1
Explanation
The stratum levels define the distance from the reference clock. A reference clock is a stratum 0 device that is assumed to be accurate and has little or no delay associated with it. Stratum 0 servers cannot be used on the network but they are directly connected to computers which then operate as stratum-1 servers. A stratum 1 time server acts as a primary network time standard.
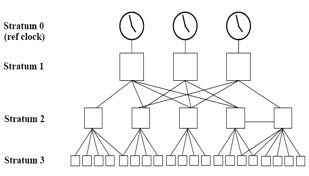
A stratum 2 server is connected to the stratum 1 server; then a stratum 3 server is connected to the stratum 2 server and so on. A stratum 2 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum 1 server. A stratum 3 server gets its time via NTP packet requests from a stratum-2 server… A stratum server may also peer with other stratum servers at the same level to provide more stable and robust time for all devices in the peer group (for example a stratum 2 server can peer with other stratum 2 servers).
NTP uses the concept of a stratum to describe how many NTP hops away a machine is from an authoritative time source. A stratum 1 time server typically has an authoritative time source (such as a radio or atomic clock, or a Global Positioning System (GPS) time source) directly attached, a stratum 2 time server receives its time via NTP from a stratum 1 time server, and so on.
Question 2
Explanation
The time kept on a machine is a critical resource and it is strongly recommend that you use the security features of NTP to avoid the accidental or malicious setting of incorrect time. The two security features available are an access list-based restriction scheme and an encrypted authentication mechanism.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/availability/high-availability/19643-ntpm.html
Question 3
Explanation
The time kept on a machine is a critical resource and it is strongly recommend that you use the security features of NTP to avoid the accidental or malicious setting of incorrect time. The two security features available are an access list-based restriction scheme and an encrypted authentication mechanism.
Reference: https://www.cisco.com/c/en/us/support/docs/availability/high-availability/19643-ntpm.html
Question 4
Explanation
If the system clock has not been set, the date and time are preceded by an asterisk (*) to indicate that the date and time are probably not correct.
Moreover, when we use “show clock” on a brand-new router (which has not been configured anything), we see the clock is set to the default value with an asterisk mask.
![]()
Therefore we can deduce this device is not configured NTP.



@digitaltut
Q4:
as you said, no answer is 100% correct. If the NTP server is unreachable from bootup, B & C is correct, but if you were unable to reach the NTP server and you a had already a valid sync before. The log messages have a “.” instead of a “*”.
That would mean that “C. The network device is not configured to use NTP” is better.
Why would a log file contain a * next to the date?
A. The network device is not configured to use NTP time stamps for logging.
B. The network device was unable to reach the NTP server when the log messages were recorded.
C. The network device is not configured to use NTP
D. The network device was receiving NTP time when the log messages were recorded
@digitaltut please verify if answer C is best choice or B.
@digitaltut Q4, I think that the correct answer is “B. The network device was unable to reach the NTP server when the log messages were recorded.”
Answer C is not correct because if we set the clock with command “clock set” there are not an *
Router#sh clock
17:22:30.812 CEST Mon Apr 4 2022
Router#sh ntp stat
%NTP is not enabled.
Router#conf t
Enter configuration commands, one per line. End with CNTL/Z.
Router(config)#exit
Router#
Apr 4 17:22:41 CEST: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Why would a log file contain a * next to the date?
A. The network device is not configured to use NTP time stamps for logging.
B. The network device was unable to reach the NTP server when the log messages were recorded.
C. The network device is not configured to use NTP
D. The network device was receiving NTP time when the log messages were recorded
The answer B is the correct answer.
Question 4
Why would a log file contain a * next to the date?
A. The network device is not configured to use NTP time stamps for logging.
B. The network device was unable to reach the NTP server when the log messages were recorded.
C. The network device is not configured to use NTP
D. The network device was receiving NTP time when the log messages were recorded
The correct answers is: C
Workaround done:
1. In GNS3 configure ntp
2. Wait for around 10 mins
3. do show clock
4. Answer C is correct
Show commands output before the NTP config:
R1(config)#do show clock
*03:27:26.845 UTC Tue Nov 22 2022
R1(config)#do show ntp stat
%NTP is not enabled.
LOG MESSAGES BEFORE NTP:
*Nov 22 03:27:28.345: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Show commands output after the NTP config:
R1(config)#ntp server 72.14.183.39
R1(config)#do show clock
03:36:10.713 UTC Tue Nov 22 2022
LOG MESSAGES AFTER NTP:
Nov 22 03:46:50.448: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Question 4
B is not the correct answer, when NTP is configured and loses it connection to the NTP server the log message will look like the following example:
.Nov 22 03:36:57.108: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
.Nov 22 03:37:55.607: %LINK-3-UPDOWN: Interface Ethernet0/1, changed state to up
.Nov 22 03:37:56.613: %LINEPROTO-5-UPDOWN: Line protocol on Interface Ethernet0/1, changed state to up
.Nov 22 03:38:00.490: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
==================
D does not make sense for me
==================
A The NTP time stamps configuration should be the following:
Router4(config)#service timestamps log datetime localtime
LOG MESSAGE using this command:
*Nov 22 03:53:50: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
*Nov 22 03:54:52: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
*Nov 22 03:55:33: %SYS-5-CONFIG_I: Configured from console by console
Reference for answer A configuration: https://www.cisco.com/E-Learning/bulk/public/tac/cim/cib/using_cisco_ios_software/cmdrefs/service_timestamps.htm
About question 2
Without ntp setup
below the default output
R2#sh clock
*19:06:38.197 CET Wed Oct 30 2024
R2#