EIGRP Questions 7
Here you will find answers to EIGRP questions – Part 7
Question 1
What action does an EIGRP router take when it cannot find a feasible successor for a network?
A. It examines the routing and neighbor tables for the next best path.
B. It transitions from passive to active state for that network and queries its neighbors.
C. It examines the topology table for a next best path.
D. It transitions from active to passive state for that network and queries its neighbors.
Answer: B
Question 2
Based on the exhibited command output, which two statements are true? (Choose two)
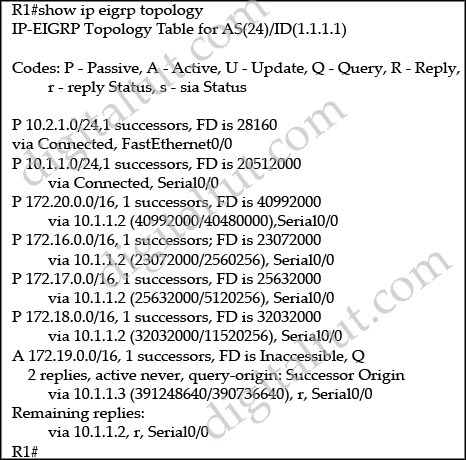
A. The EIGRP network is stable.
B. The router at 10.1.1.3 has not replied to the R1 query packet.
C. The route to 172.19.0.0/16 is undergoing recomputation.
D. The route to 172.19.0.0/16 is stuck-in-active.
E. R1 has sent a query packet to 10.1.1.2.
Answer: C E
Explanation
The route to 172.19.0.0/16 is in Active state (letter “A”). The route is in Active state when a router is undergoing a route recomputation -> C is correct.
Also, the lower letter “r” in “via 10.1.12, r, Serial0/0” indicates R1 has sent a query to 10.1.1.2 and is waiting for a reply -> E is correct.
Question 3
A network administrator would like to configure an EIGRP router as a stub router that advertises directly connected and summary routes only. What command must the administrator issue to accomplish this?
A. eigrp stub
B. eigrp stub connected
C. eigrp stub summary
D. eigrp stub connected static
E. eigrp stub receive-only
Answer: A
Explanation
The command “eigrp stub” is equivalent to the command “eigrp stub connected summary” because the connected and summary options are enabled by default.
Question 4
Which two among the following are used to indicate external type of route in routing table? (Choose two)
A. D EX
B. IA
C. E2
D. R E2
E. i L2
Answer: A C
Question 5
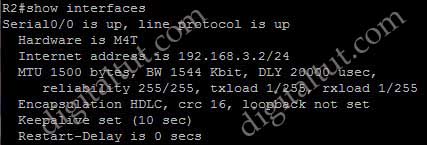
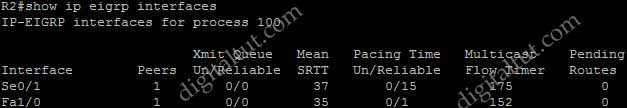
Which show command will display the two values used in the calculation of the EIGRP metric?
A. show protocol
B. show ip eigrp interface
C. show interface
D. show ip eigrp neighbor
Answer: C
Explanation
First, recall the formula of calculating EIGRP metric:
metric = [K1 * bandwidth + (K2 * bandwidth)/(256 – load) + K3 * delay] * [K5/(reliability + K4)]
The four outputs of the above commands are shown below:
+ show protocols: this command does not show any information about 4 values of EIGRP metric.
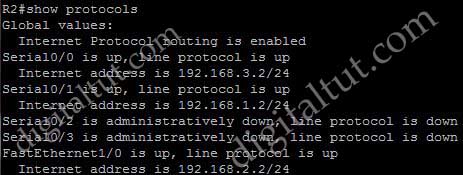
+ show interfaces: this command has all 4 values of metric. This is the most suitable answer.
+ show ip eigrp interfaces: no information about values of metric.
+ show ip eigrp neighbor: this command does not have any values of metric.
Note: As you remember, we have to specify 5 values when redistributing into EIGRP. But notice that these are not the five “K” values.
Question 6
A network administrator is troubleshooting an EIGRP configuration across a discontiguous network. What must the administrator do to ensure the routers have the correct routing information?
A. Nothing, EIGRP supports discontiguous networks by default.
B. The administrator must disable automatic summarization with the command no auto-summary.
C. The administrator must enable manual summarization with the command ip summary-address.
D. The administrator must enable classless routing with the command ip classless.
E. The administrator must specify a default network with the command ip default-network.
Answer: B
Question 7
What is the purpose of the eigrp stub configuration command?
A. to increase scalability by limiting the EIGRP query range
B. to reduce the size of the routing table by blocking the D EX (External EIGRP) routes into the EIGRP stub router
C. to reduce the convergence time by enabling the EIGRP stub router to propagate the EIGRP queries from the EIGRP hub router
D. to reduce the convergence time by enabling the EIGRP stub router to also perform query requests to the EIGRP hub router
Answer: A
Explanation
Stub router provides network architects with greater flexibility for designing EIGRP networks by enabling improved control over traffic flows and limitations of query flooding.
Question 8
Which EIGRP packet statement is true?
A. On high-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 5 seconds for neighbor discovery.
B. On low-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 15 seconds for neighbor discovery.
C. Reply packets are multicast to IP address 224.0.0.10 using RTP.
D. Update packets route reliable change information only to the affected routers.
E. Reply packets are used to send routing updates.
Answer: D
Explanation
The default hello timer for a high-speed broadcast network link is 5 seconds and the hold-down timer is 15 seconds whereas the default timers for slow-speed NBMA link are 60 seconds hello and 180 seconds dead. A slow-speed NBMA link is classified as any NBMA link with speeds equal to or less than 1544Kbps (A single T1) -> A and B are not correct.
EIGRP sends update packets using multicast address 224.0.0.10 but it acknowledges updates using unicast hello packets with no data (also uses RTP) -> C is not correct.
Unlike OSPF which requires calculation of all routes when the topology changes, EIGRP only sends routing updates to affected routers -> D is correct.
Reply packets (for hello packets) are just used to acknowledge the hello packets with no data -> E is not correct.
Question 9
Refer to the exhibit. What happens when the router stops receiving advertisements for the 10.1.2.0/24 network?
| Router# show ip route C 10.1.3.0/24 is directly connected, Serial2 D 10.1.2.0/24 [90/10537472] via 10.1.1.2, 00:23:24, Serial1 D 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, 00:23:20, Null0 C 10.1.1.0/24 is directly connected, Serial1 S 192.168.20.0/24 is directly connected, Ethernet0 |
A. The summary route will be removed from the table.
B. The summary route will remain in the table.
C. The more specific routes will be advertised from the table.
D. 10.1.2.0/24 will still be advertised but packets destined for it will be dropped when they reach this router.
Answer: B
Explanation
There are two cases for the line “D 10.0.0.0/8 is a summary, 00:23:20, Null0” to appear in the routing table:
+ By the “auto-summary” command under EIGRP mode.
+ By the “ip summary-address eigrp AS-number 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0″ under interface mode.
When we create a summary route, one summary route will be created automatically pointing towards Null0 interface. This is a loop prevention mechanism.
Even when the router stops receiving advertisements for the 10.1.2.0/24 network, other networks that belong to 10.0.0.0/8 still exist so the summary route will still remain in the routing table. The summary route only disappears only when all of its related networks are turned off.
For more information about summarization & Null0 interface, please read my Auto and Manual Summary Routes to Null0 with EIGRP tutorial.
Question 10
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured on all routers in the network. On the basis of the output provided, which statement is true?
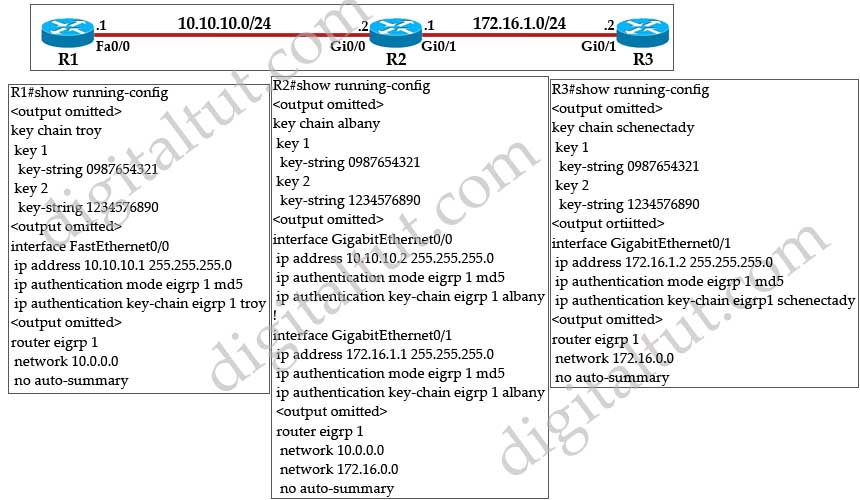
A. Because the key chain names do not match, router R1 will not be able to ping routers R2 and R3.
B. Because the key strings do not match, router R1 will not be able to ping routers R2 and R3.
C. Because authentication is misconfigured on interfaces Gi0/0 and Gi0/1 on router R2, router R1 will not be able to ping routers R2 and R3.
D. Because autosummarization needs to be turned on for EIGRP on all routers, router R1 will not be able to ping routers R2 and R3.
E. Router R1 will be able to ping routers R2 and R3.
Answer: E



Q8 Hi everybody,
Which EIGRP packet statement is true?
A. On high-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 5 seconds for neighbor discovery.
B. On low-speed links, hello packets are broadcast every 15 seconds for neighbor discovery.
C. Reply packets are multicast to IP address 224.0.0.10 using RTP.
D. Update packets route reliable change information only to the affected routers.
E. Reply packets are used to send routing updates.
In this question, I must say that options C and D are correct. RTP is a Cisco proprietry protocol, used in EIGRP to manage the communication of messages between EIGRP-Speaking Routers.Reliable Transport or Delivery of EIGRP packets means Acknowledgement is required from the receiving Router and the packet should be delivered in order. Updates, Queries and Replies are reliable eigrp packet, so they use RTP. Please read the following article and correct me If I am wrong:
URL: http://www.networkpcworld.com/rtp-reliable-transport-protocol-of-eigrp/
you are wrong as this is not multicast – ack, reply are always unicast so C – is wrong
I thing that A could be also correct
D – correct