LISP Lab
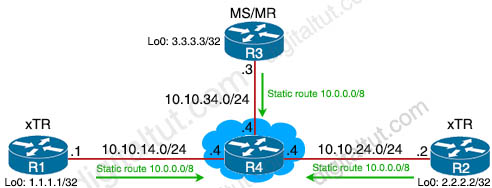
In this lab we will configure a simple topology so that the Loopback0 interface on R1 can ping the Loopback0 interface on R2 via LISP.
IOS version used in this lab: 15.4(1)T
Initial config:
| R1 hostname R1_xTR int lo0 ip address 1.1.1.1 255.255.255.255 int e0/0 ip address 10.10.14.1 255.255.255.0 no shut ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.10.14.4 |
R2 hostname R2_xTR int e0/0 ip address 10.10.24.2 255.255.255.0 no shut int lo0 ip address 2.2.2.2 255.255.255.255 ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.10.24.4 |
| R3 hostname R3_MS_MR int e0/0 ip address 10.10.34.3 255.255.255.0 no shut ip route 10.0.0.0 255.0.0.0 10.10.34.4 |
R4 hostname R4_Underlay int e0/0 ip address 10.10.14.4 255.255.255.0 no shut int e0/1 ip address 10.10.24.4 255.255.255.0 no shut int e0/2 ip address 10.10.34.4 255.255.255.0 no shut |
Notice that R4 does not have any static route. It acts as an underlay network (includes multiple WAN transport technologies such as MPLS, broadband, 4G, Internet connections…).
| This lab is created with IOUWeb so you can download the lab file here. The final configs of all routers can be downloaded here. |
LISP related config:
| R1 (xTR) router lisp database-mapping 1.1.1.0/24 10.10.14.1 priority 1 weight 100 ipv4 itr ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.10.34.3 ipv4 etr ipv4 etr map-server 10.10.34.3 key tut_siteA |
R2 (xTR) router lisp database-mapping 2.2.2.0/24 10.10.24.2 priority 1 weight 100 ipv4 itr ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.10.34.3 ipv4 etr ipv4 etr map-server 10.10.34.3 key tut_siteB |
| R3 (MS/MR)
lisp site siteA lisp site siteB ip lisp map-server |
R4 (Underlay) No LISP related configuration needed on R4. |
R1 configuration
The “database-mapping 1.1.1.0/24 10.10.14.1 priority 1 weight 100” is used to configure the LISP database mapping, which describes the Endpoint Identifier-to-Routing locator (EID-to-RLOC) mapping relationship. Therefore in the above command, the “1.1.1.0/24” is the EID while the “10.10.14.1” is the RLOC. We can assign multiple different EIDs to the same RLOC (which will be discussed later in this lab). In order to see the LISP database mapping table, we can use the “show ip lisp database” command:
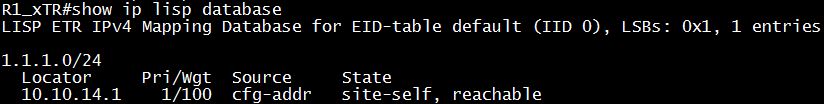
The “priority” and “weight” are used for priority and load balancing but they will not be discussed in detail here to keep this lab simple.
When we define an EID to RLOC mapping (via the “database-mapping” command) on R1, it sends a LISP “Map Register” message to the Map-Server (MS). MS uses this information to populate its EID to RLOC mapping table and replies back with a “Map Notify” message. MS does not share this information to anyone else.
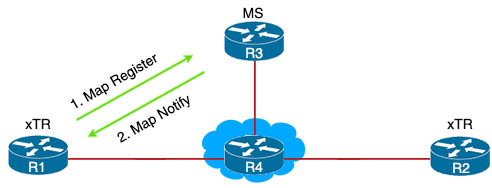
Next we need to configure both LISP Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR) and Egress Tunnel Router (ETR) roles for R1.
ITR is the function that maps the destination EID to a destination RLOC and then encapsulates the original packet with an additional header that has the source IP address of the ITR RLOC and the destination IP address of the RLOC of an Egress Tunnel Router (ETR). After the encapsulation, the original packet become a LISP packet.
To do this function, R1 needs to “resolve” the EID prefix to RLOC so R1 needs to query the LISP map-resolver . Therefore we have to tell R1 the IP address of the map-resolver on R3 via the “ipv4 itr map-resolver 10.10.34.3” command.
Note: Map-resolver (MR) receives and processes the EID-to-RLOC mapping lookup queries and provides the mappings to requester
ETR is the function that receives LISP encapsulated packets, decapsulates them and forwards to its local EIDs. This function also requires EID-to-RLOC mappings so we need to point out an “map-server” IP address and the key (password) for authentication.
Note: Map Server (MS) processes the registration of authentication keys and EID-to-RLOC mappings. ETRs sends periodic Map-Register messages to all its configured Map Servers.
ITR and ETR are often included in a single device and it is called a xTR device.
The same configuration is used on R2 so we can ignore it. Let’s discuss about R3 configuration.
R3 configuration
R3 acts as a Map Resolver and Map Server so besides configuring R3 as a Map Server and Map Resolver (via the “ip lisp map-server” & “ip lisp map-resolver” commands), we have to define our LISP sites and the EID prefixes that are associated with them. An authentication key should also be used for each site and it must match the key configured on the xTR devices.
After a few seconds we can verify the LISP sites configured on R3 with the “show lisp site” command:
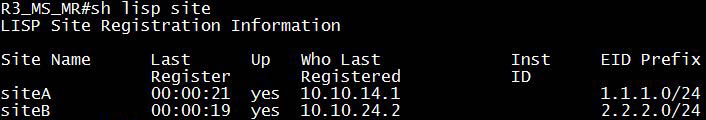
We see both R1 & R2 have registered (via “Who Last Registered” field) their sites to R3 as they have been configured before configuring R3.
An import thing to notice that there is no configuration about LISP is required on R4 which simulates the WAN connection between LISP devices. Therefore nothing is required on the WAN service provider side.
Another important table we should know is the LISP Mapping Cache:
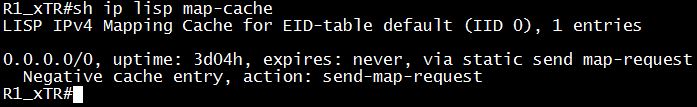
At this time when the communication between R1 & R2 has not been established, we only have the default entry in the map-cache. When the device reaches this entry, it does an action: send a map request to the the MS/MR to ask for the information about the EID it is trying to reach. In other words, it is trying to “pull” the information it needs.
Therefore after a ping, R1 received the EID of 2.2.2.0/24 from the MS/MR:
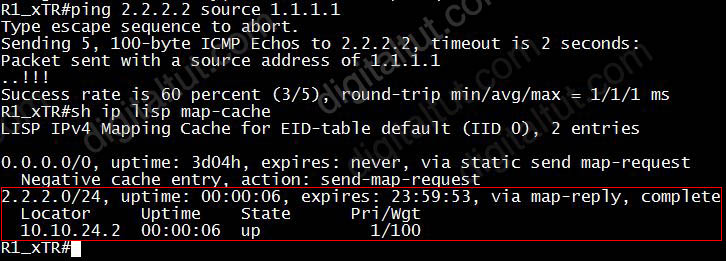
Maybe you also noticed that the first two ping packets failed while three last ping packets succeeded. This is because at the beginning R1 has not had information about 2.2.2.2 in its mapping cache so it must send a Map-Request message to its configured map-resolver and then discard the original packet. After receiving the Map-Reply message from the Map-resolver, it creates a new mapping cache entry of 2.2.2.0/24 as shown above which is used for next ping packets.
If we want to retest this, we can clear the map-cache with the command clear ip lisp map-cache.



Thx 9tut!
I followed the laboratory exactly. I can see the two registered sites from the MR / MS router (site a-b), but from router r1 I do not ping… I use gns3 with ios cisco7200 15.x with lisp support
@rob: We have just uploaded the final configs here: https://www.digitaltut.com/download/LISP_Basic_6_routers_config_final.zip so that you can verify.
this lab works with eve-ng?
@capitao_caverna: Yes, it does.
hi. how do I open the lab files uploaded here? Thanks!
While setting up the same LISP lab via GNS3 with Cisco 7200 the configuration in R3 is slightly difference from the config listed.
Following is the configuration for SiteA.
R3 (MS/MR)
Router(config)#router lisp
Router(config-router-lisp)#ipv4 map-server
Router(config-router-lisp)#ipv4 map-resolver
Router(config-router-lisp)#site siteA
Router(config-router-lisp-site)#eid-prefix 1.1.1.0/24
Router(config-router-lisp-site)#authentication-key tut_siteA
Router(config-router-lisp-site)#exit
Router#sh lisp site
LISP Site Registration Information
Site Name Last Up Who Last Inst EID Prefix
Register Registered ID
siteA 00:00:47 yes 10.10.14.1 1.1.1.0/24
From the LISP related config:
The ip map-server and ip lisp map-resolver command is not available and is avilable under ipv4/6
The site configuration also need to enter lisp configuration mode before configuring the site
Same as for eid-prefix and authentication-key.
Router(config-router-lisp)#ipv4 ?
alt-vrf Activate LISP-ALT functionality in VRF
etr Configures a LISP Egress Tunnel Router (ETR)
itr Configures a LISP Ingress Tunnel Router (ITR)
map-cache-limit Configures maximum size of map-cache
map-cache-persistent Dump map-cache onto flash, making it persistent across
reboots
map-request-source Configures inner header source address in Map-Request
message
map-resolver Configures a LISP Map Resolver (MR)
map-server Configures a LISP Map Server (MS)
path-mtu-discovery Path MTU discovery
proxy-etr Configures a LISP Proxy Engress Tunnel Router (PETR)
proxy-itr Configures a LISP Proxy Ingress Tunnel Router (PITR)
route-import Import RIB routes by a routing protocol into LISP
solicit-map-request Configure Solicit-Map-Request handling
use-petr Encapsulate to Proxy ETR when matching forward-native
entry
Dears, does the ENCOR test have labs?
I implemented this lab on GNS3 and i86bi-linux-l3-adventerprisek9-ms.155-2.T. image, it works perfect!! thank you 9tut!
Is this still included on the latest exam topic?
HELLO TUT is these labs are in the exam?
I got it working perfectly with CML.
I used IOL for all routers EXCEPT for R3, which I had to use IOSv for R3.
Apparently, IOL doesn’t support LISP properly for our configuration.
IOSv, however, does support everything.
I got it working perfectly with CML using ISOv for all the routers and no a single issue. Works perfectly with these images