EIGRP Questions
Here you will find answers to EIGRP questions
Question 1
Which three statements about the EIGRP routing protocol are true? (Choose three)
A – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.9
B – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.10
C – EIGRP supports five generic packet types. including hello, update, query, reply, and ACK packets
D – EIGRP supports five generic packet types, including hello, database description (DBD), link-state request (LSR), link-state update (LSU), and LSAck
E – E. EIGRP will form a neighbor relationship with another peer even when their K values are mismatched
F – A. EIGRP will not form a neighbor relationship with another peer when their K values are mismatched
Answer: B, C, F
Question 2
After DUAL calculations, a router has identified a successor route, but no routes have qualified as a feasible successor. In the event that the current successor goes down, what process will EIGRP use in the selection of a new successor?
A – EIGRP will find the interface with the lowest MAC address
B – The route will transition to the active state
C – The route will transition to the passive state
D – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest feasible distance (FD)
E – EIGRP will automatically use the route with the lowest advertised distance (AD)
Answer: B
Explanation
When a route (current successor) goes down, the router first checks its topology table for a feasible successor but it can’t find one. So it goes active on the that route to find a new successor by sending queries out to its neighbors requesting a path to the lost route.
Question 3
Refer to the exhibit. Routers R1 and R2 have established a neighbor relationship and are exchanging routing information. The network design requires that R1 receive routing updates from R2, but not advertise any routes to R2. Which configuration command sequence will successfully accomplish this task?
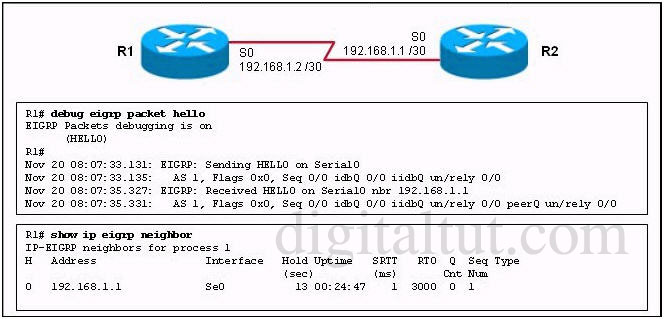
A – R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
B – R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# passive-interface serial 0
C – R1(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
D – R2(config)# access-list 20 deny any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 out serial 0
E – R1(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R1(config)# router eigrp 1
R1(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
F – R2(config)# access-list 20 permit any
R2(config)# router eigrp 1
R2(config-router)# distribute-list 20 in serial 0
Answer: C
Explanation
We can not use passive-interface to accomplish this task because the “passive-interface…” command (in EIGRP or OSPF) will shut down the neighbor relationship of these two routers (no hello packets are exchanged). And to filter routing updates we should configure a distribute list on R1 with an access list that deny all and apply it to the outbound direction so that R1 can receive but can not send routing updates.
Question 4
EIGRP has been configured to operate over Frame Relay multipoint connections. What should the bandwidth command be set to?
A – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection multiplied by the number of circuits
B – the CIR rate of the lowest speed connection
C – the CIR rate of the highest speed connection
D – the sum of all the CIRs divided by the number of connections
Answer: A
Explanation
If the multipoint network has different speeds allocated to the VCs, take the lowest CIR and simply multiply it by the number of circuits. This is because in Frame-relay all neighbors share the bandwidth equally, regardless of the actual CIR of each individual PVC, so we have to get the lowest speed CIR rate and multiply it by the number of circuits. This result will be applied on the main interface (or multipoint connection interface).
Question 5
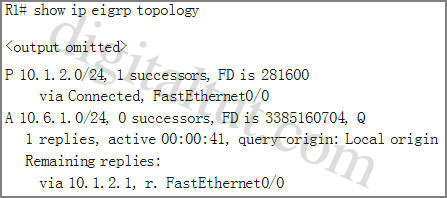
Refer to the exhibit. EIGRP is configured on all routers in the network. On a basis of the show ip eigrp topology output provided, what conclusion can be derived?
A – Router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 out of interface FastEthernet0/0
B – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out before it declares the neighbor unreachable
C – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 to the hello message sent out inquiring for a second successor to network 10.6.1.0/24
D – Router R1 is waiting for a reply from the neighbor 10.1.2.1 in response to the query sent out about network 10.6.1.0/24
Answer: D
Explanation
From the output, we notice that there is an active route (A) and the reply status flag (r) was set. An active EIGRP route is the state when a network change occurs and a feasible successor is not found by a EIGRP router for a given route (10.6.1.0/24); and the reply status flag (r) means that R1’s queries were sent out to the neighbors asking for routing information to the 10.6.1.0/24 network but hasn’t received a reply yet. Therefore the answer A – router R1 can send traffic destined for network 10.6.1.0/24 is not correct because router R1 can’t find a path to that network. Answers B and C are not correct because R1 doesn’t send a hello message but a query asking for routing information to the desired network.



To form a neighbor relationship in EIGRP, There are two conditions which need to be verified
1. AS no should match
2. K-values shoud match
If any condition is found to be mismatch ,then there is no neighbor relationship
hence below answers are correct
Reply for
Which three statements about the EIGRP routing protocol are true? (Choose three)
A – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.9
B – EIGRP sends periodic hello packets to the multicast IP address 224.0.0.10
C – EIGRP supports five generic packet types. including hello, update, query, reply, and ACK packets
D – EIGRP supports five generic packet types, including hello, database description (DBD), link-state request (LSR), link-state update (LSU), and LSAck
E – E. EIGRP will form a neighbor relationship with another peer even when their K values are mismatched
F – A. EIGRP will not form a neighbor relationship with another peer when their K values are mismatched
Answer: B, C, F
TH answer should be B,C,E .
because the K values is not a condition for neighbor relationship only the AS number should match.
anyway I tried it on GNS3 by changing the BW and still the relation is valid.
@Nishant
Stop confusing people.
K values must match to form neighborship.
All of them must match. No exceptions.
The link Bandwidth is not a K Value. It is an attribute of the link.
The K value that sets how important Bandwidth is for the metrics calculator is K1. It is set to 1 by default.
So, for question 1 should be Answer: B, C, F.
You need to configure the K-values in router configuration mode. What you did is change the bandwidth value on the interface which is not the way.
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 ?
K1
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 1 ?
K2
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 1 0 ?
K3
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 1 0 1 ?
K4
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 1 0 1 0 ?
K5
R2(config-router-af)#metric weights 0 1 0 1 0 0
I have a small question